Urethral Stricture
Urethral Stricture
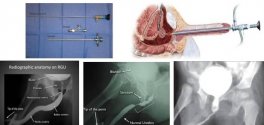
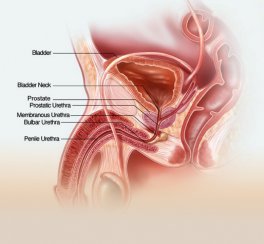
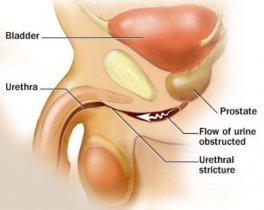
The diameter of the urethra is about 6-10 mm in diameter, though in the bulbar urethra to 2 cm However, due to damage and fibrosis, the diameter of the duct is less than normal, which is referred to as Urethral Stricture Causes of urethral stenosis Can be acquired or congenital.

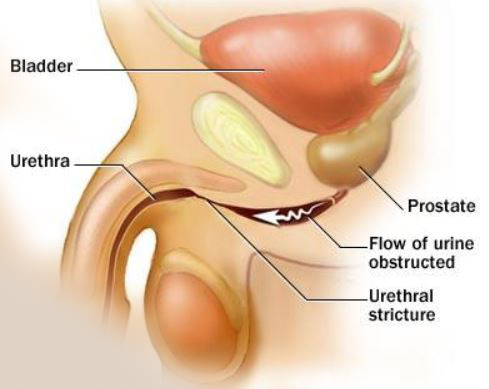
Urethral Stricture causes :
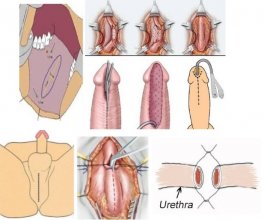
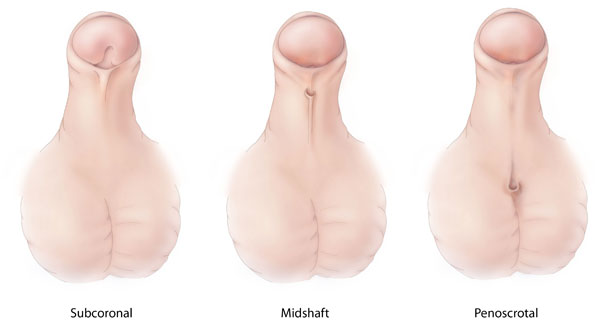
1. Hypospadiasis:
is the most common congenital malformation of the penis, and about 1 infant is affected by 300 births and has 3 types.
- The hole of the duct is below the tip of the penis.
- The hole in the duct is in the body of the penis.
- The duct hole is located at scrotom between two testicles.
It can be accompanied by Urethral stricture.
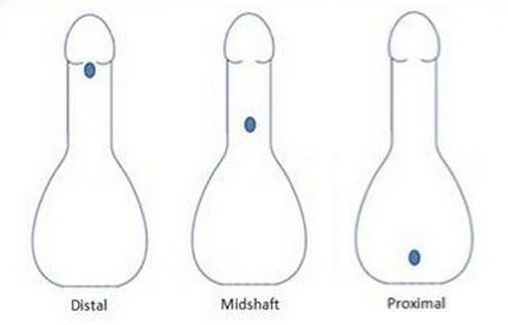
2. Epispadosis:
in which the bladder or urethra is uncovered at birth, can change from the bladder to the end of the penis at dorsal surface of penis.
- In the hypospadias, the hole in the front of the penis and in the epispadiosis is a hole in the back of the penis.
- Acquired causes
- Impact or damage such as injury to the pelvis due to accidents resulting in damage to the posterior urethra. Damage to the perinea that damages the bulbar urethra and damage to the penis during intercourse or external injury.
- Infection that can be the most common cause.
- However, sclerosis (BXO) is characterized by whiteness and tingling of the tip of the penis.
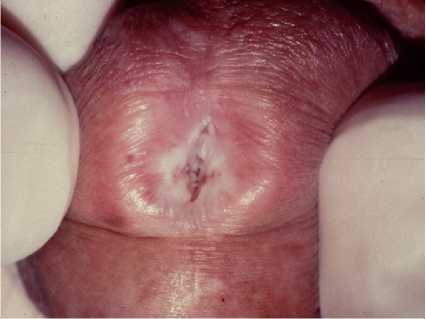
- Surgery for the repair of hypospadias.
- The manipulation of the urethra(for example, surgical procedures from the urethra, or endoscopy of the urethra and catheter in the urethra, which is especially seen in patients undergoing heart surgery, is sometimes seen.)
- Urethral cancer
- Un specified causes (there is no cause or harm)
Signs of urethral stricture:
The following symptoms are commonly seen in men over 50 years of age due to benign prostatic hypertrophy, but in young people it can be a sign of urethral stricture.
- Reduced urine flow, especially compared to the past
- Spread or spray around while urinating
- Disconnect urine while urinating(dribbling)
- Taking urine while urinating(straining)
- Delay in beginning urination (the person wants to urinate but does not go out for a few seconds or a short time in the urine toilet)(Hesitency)
- Drop of urine after the completion of the urination and dirty underwear(post void dribbling)
- Seek early to go to the urine(frequency)
- It is not able to keep urine (ie, the patient should go to the toilet immediatelyand can not tolerate). (uregency)
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Abscess and accumulation of infection in the perineum or testicles
 زبان فارسی
زبان فارسی